If you find yourself relying heavily on your smartphone’s GPS when roaming outdoors, Microsoft Research’s newest navigational innovation is likely to alleviate one of the main frustrating limitations of current GPS technology. Researchers at Microsoft are developing a new system that will provide highly accurate GPS-like mapping indoor environments. The team behind the technology believes that their new system will have a navigational impact comparable to innovations made with GPS over the past several years.
This week, Dimitrios Lymberopoulos, Jie Liu, and Bodhi Priyantha of Microsoft Research will be presenting a paper on the new technology titled “FM-Based Indoor Localization.” The indoor navigational system was built upon research already done to test out mapping through Wi-FI signals, which would enable any smartphone currently on the market to adopt the system. The researchers found, however, that the Wi-Fi signal was both inconsistent and susceptible to disruption by common building materials.
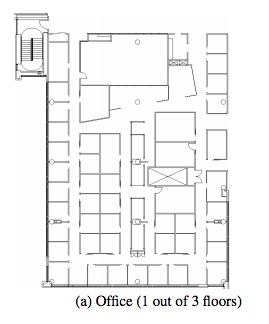
In order to improve the stability of the signal for indoor navigation, the researchers deployed a system using commercial FM-radio signals that proved to be much more stable and accurate over previous Wi-Fi-only technology. Microsoft researchers eventually paired the Wi-Fi and FM-radio signals into a single, highly accurate system. When testing in an office environment, the team was able to accurately identify particular rooms, increasing the accuracy of the system from 92 to as high as 98 percent by combining the signals.
Microsoft’s new technology could be used not only to improve the way we find our way around shopping centers and office buildings, but also greatly improve navigational systems for the handicapped. One research team at the University of Nevada in Reno have been developing a navigational system for the blind that utilizes basic landmarks in architectural blueprints to provide directional audio cues – a system that could likely be significantly improved by the Microsoft Research technology.
The team expects that with a minimal software update, most smartphones currently on the market will be able to utilize the Wi-Fi/FM signals to begin navigating indoor environments in the near future.